If you're diving into the world of mushroom cultivation, there's one tool that stands out as…
What Is the Difference Between Mushrooms and Toadstools
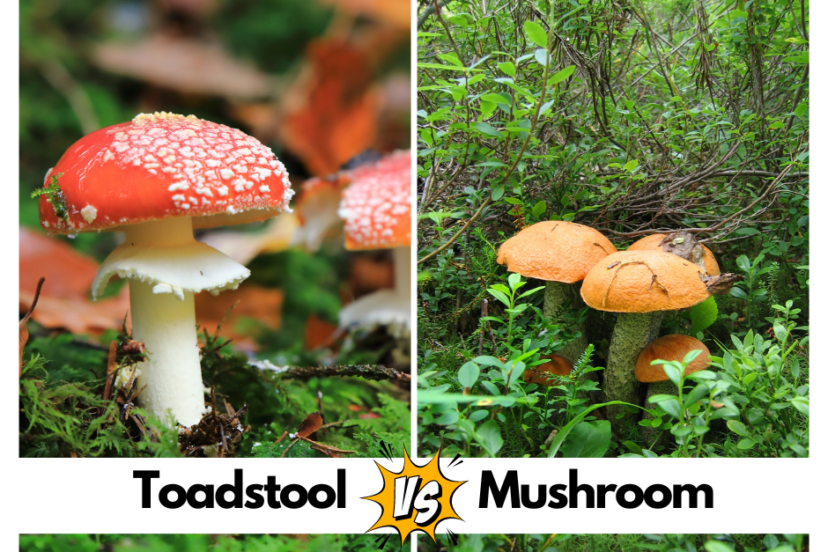

The world of fungi is a fascinating realm, rich with a diverse array of shapes, colors, and forms. Among the many captivating inhabitants of this kingdom are mushrooms and toadstools. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they do have distinct differences that set them apart. In this article, we will delve into the dissimilarities between toadstools vs mushroom, shedding light on their unique characteristics and dispelling some common misconceptions.
Understanding the Terminology: Toadstool vs Mushroom
Before we delve into the differences, let’s clarify what exactly these terms refer to. Both mushrooms and toadstools are types of fungi, and they share many similarities in terms of structure and growth. The “toadstool” is usually used to describe fungus with a stem and a cap, or fungi that are poisonous, whereas “mushroom” is used to describe edible fungi. Besides, the distinction between the two often lies in their cultural connotations, and, to some extent, their scientific classification as well.
Mushroom
The term “mushroom” is commonly used to describe a wide variety of edible and non-edible fungi with a distinctive cap and stem structure. Mushrooms have been an integral part of culinary traditions across the globe, finding their way into an array of dishes, from savory stews to gourmet delicacies. They are typically prized for their taste, texture, and nutritional value.
Toadstool
The term “toadstool,” on the other hand, is often associated with inedible or toxic fungi. While there is no strict scientific distinction between a toadstool and a mushroom, the term “toadstool” tends to evoke caution due to its historical use as a way to differentiate between fungi that are safe to eat and those that are potentially harmful. Toadstools are often depicted in fairy tales and folklore as whimsical, sometimes poisonous, growths.
Distinguishing Features: Mushroom vs Toadstool
While the terms “toadstool” and “mushroom” are not always used consistently across different cultures and regions, there are some general features that can help differentiate between the two.

-
Cap Shape and Texture:
Mushrooms typically have a cap that opens up and may vary in shape, ranging from convex to flat or even irregular. Toadstools, on the other hand, often have a cap that remains closed, resembling a parasol or an umbrella. The cap of a toadstool may be more ornate or frilly compared to the relatively simpler cap of a mushroom.
-
Gills vs Pores:
Mushrooms commonly have gills on the underside of the cap, which are thin, radiating structures that produce and release spores. Toadstools may have gills, but they can also have pores. Pores are tiny openings on the underside of the cap through which spores are released. Some toadstools, like the iconic fly agaric (Amanita muscaria), have white, closely packed pores.
-
Habitat and Association:
Mushrooms frequently appear in various habitats, such as forests, grasslands, and even urban environments. People cultivate numerous edible mushrooms for culinary intentions. Because of their historical connection with toxicity, toadstools tend to have a stronger association with woodland environments and are often depicted as growing near the bases of trees.
-
Cultural and Culinary Significance:
As mentioned earlier, cultural and culinary factors can also influence the usage of the terms “toadstool” vs. “mushroom.” People celebrate mushrooms for their role in cuisine and various cultures have made them a staple ingredient. Because of their potentially toxic nature, people tend to treat toadstools with caution and are less likely to include them in culinary practices.
Misconceptions and Clarifications
It’s important to note that not all mushrooms are safe to eat, and not all toadstools are toxic. The terms “toadstool” and “mushroom” do not provide a foolproof way of determining whether a fungus is edible or not. Proper identification is crucial when foraging for wild fungi, regardless of whether you use the term “toadstool” or “mushroom.”

In some regions, the terms “toadstool” and “mushroom” are used interchangeably, and the distinction between the two is less emphasized. Scientifically speaking, both mushrooms and toadstools belong to the same fungal group and are subject to similar classification and naming conventions.
Final Thoughts on Toadstool vs Mushroom
The difference between toadstools and mushrooms lies not only in their physical characteristics but also in their cultural associations and historical usage. While the terms “toadstool” and “mushroom” may help convey a general idea about a fungus’s edibility or toxicity, they do not provide a definitive guide for identification. To ensure your safety and enjoyment when foraging or consuming fungi, relying on proper scientific identification is crucial. Use field guides, expert advice, and reliable resources. Whether you prefer to use the term “toadstool” or “mushroom,” always prioritize caution and knowledge to fully appreciate the intriguing world of fungal diversity.






Medicinal mushrooms contain compounds such as beta-glucans, triterpenoids and polysaccharides which provide antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Consuming a blend of multiple mushrooms, as found in provides synergistic benefits due to their complementary effects. The psilocybe make it easy to obtain the benefits of mushrooms as part of your daily routine.